Ultimate guide to DoS(Denial of Service) Attacks
Inthis tutorial, we will introduce you towhat denial of service attack is, how it is performed and how you can protect against such attacks.
What is DoS Attack?
DoS is the acronym for Denial of Service. It is an attack that is aimed at either cutting off access to a resource such as a web site/app/service etc or making it extremely slow. This type of attack is usually implemented by hitting the target resource such as a web server with too many requests at the same time. This results in the server failing to respond to all the requests. The effect of this can either be crashing the servers or slowing them down.
Types of Dos Attacks
There are two types of Dos attacks namely;
- DoS– this type of attack is performed by a single host
- Distributed DoS– this type of attack is performed by a number of compromised machines that all target the same victim. It floods the network with data packets.
How DoS attacks work
Let’s look at how DoS attacks are performed and the techniques used. We will look at five common types of attacks.
Ping of Death
The ping command is usually used to test the availability of a network resource. It works by sending small data packets to the network resource. The ping of death takes advantage of this and sends data packets above the maximum limit (65,536 bytes) that TCP/IP allows. TCP/IP fragmentation breaks the packets into small chunks that are sent to the server. Since the sent data packages are larger than what the server can handle, the server can freeze, reboot, or crash.
Smurf
This type of attack uses large amounts of Internet Control Message
Protocol (ICMP) ping traffic target at an Internet Broadcast Address.
The reply IP address is spoofed to that of the intended victim. All the
replies are sent to the victim instead of the IP used for the pings.
Since a single Internet Broadcast Address can support a maximum of 255
hosts, a smurf attack amplifies a single ping 255 times. The effect of
this is slowing down the network to a point where it is impossible to
use it.
A buffer is a temporal storage location in RAM that is used to hold data so that the CPU can manipulate it before writing it back to the disc. Buffers have a size limit. This type of attack loads the buffer with more data that it can hold. This causes the buffer to overflow and corrupt the data it holds. An example of a buffer overflow is sending emails with file names that have 256 characters.
Teardrop
This type of attack uses larger data packets. TCP/IP breaks them into fragments that are assembled on the receiving host. The attacker manipulates the packets as they are sent so that they overlap each other. This can cause the intended victim to crash as it tries to re-assemble the packets.
SYN attack
SYN is short form for Synchronize. This type of attack takes advantage of the three-way handshake to establish communication using TCP. SYN attack works by flooding the victim with incomplete SYN messages. This causes the victim machine to allocate memory resources that are never used and deny access to legitimate users.
DoS attack tools
The following are some of the tools that can be used to perform DoS attacks.
- Nemesy– this tool can be used to generate random packets. It works on windows. This tool can be downloaded from http://packetstormsecurity.com/files/25599/nemesy13.zip.html . Due to the nature of the program, if you have an anti virus, it will most likely be detected as a virus.
- Land and LaTierra– this tool can be used for IP spoofing and opening TCP connections
- Blast– this tool can be downloaded from http://www.opencomm.co.uk/products/blast/features.php
- Panther- this tool can be used to flood a victim’s network with UDP packets.
- Botnets– these are multitudes of compromised computers on the internet that can be used to perform a distributed denial of service attack.
Hacking Activity: Ping of Death
We will assume you are using Windows for this exercise. We will also assume that you have at least two computers that are on the same network. DOS attacks are illegal on networks that you are not authorized to do so. This is why you will need to setup your own network for this exercise.Open the command prompt on the target computer
Enter the command ipconfig. You will get results similar to the ones shown below
For this example, we are using Mobile Broadband connection details. Take note of the IP address. Note: for this example to be more effective, you must use a LAN network.
Switch to the computer that you want to use for the attack and open the command prompt
We will ping our victim computer with infinite data packets of 65500
Enter the following command
ping 10.128.131.108 –t -65500
- “ping” sends the data packets to the victim
- “10.128.131.108” is the IP address of the victim
- “-t” means the data packets should be sent until the program is stopped
- “-l” specifies the data load to be sent to the victim
Flooding the target computer with data packets doesn’t have much effect on the victim. In order for the attack to be more effective, you should attack the target computer with pings from more than one computer.
The above attack can be used to attacker routers, web servers etc.
If you want to see the effects of the attack on the target computer, you can open the task manager and view the network activities.
- Right click on the task bar
- Select start task manager
- Click on the network tab
- You will get results similar to the following
Hacking Activity: Launch a DOS attack
In this practical scenario, we are going to use Nemesy to generate data packets and flood the target computer, router or server.
As stated above, Nemesy will be detected as an illegal program by your anti-virus. You will have to disable the anti-virus for this exercise.- Download Nemesy from http://packetstormsecurity.com/files/25599/nemesy13.zip.html
- Unzip it and run the program Nemesy.exe
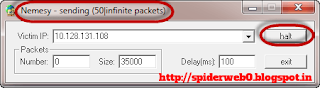
- You will get the following interface
HERE,
- 0 as the number of packets means infinity. You can set it to a desired number if you do not want to send infinity data packets
- The size field specifies the data bytes to be sent and the delay specifies the time interval in milliseconds.
You should be able to see the following results
The title bar will show you the number of packets sent
Click on halt button to stop the program from sending data packets.
You can monitor the task manager of the target computer to see the network activities.
Summary
- A denial of service attack’s intent is to deny legitimate users access to a resource such as a network, server etc.
- There are two types of attacks, denial of service and distributed denial of service.
- A denial of service attack can be carried out using SYN flooding, Ping of Death, Teardrop, Smurf or buffer overflow
- Security patches for operating systems, router configuration, firewalls and intrusion detection systems can be used to protect against denial of service attacks.
Blog By S.Adhikari